Treatment of scoliosis in Turkey
Scoliosis Treatment in Turkey
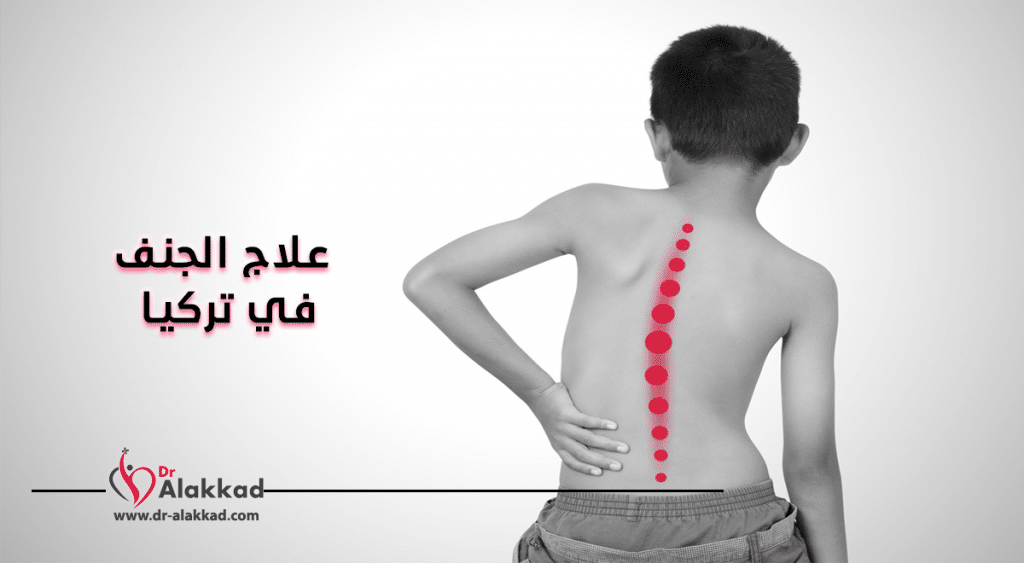
Spinal curvature, known as “scoliosis,” is a condition most often diagnosed during adolescence. Scoliosis, which develops as the vertebrae curve to the right or left for various reasons—or twist around their own axis—can begin at an early age and seriously affect a person’s life if left untreated.
What is scoliosis?
Scoliosis is the oldest known spinal deformity, with an incidence ranging from 0.2% to 6%. It can develop due to various causes such as trauma and congenital growth disorders, and in 80% of scoliosis cases the cause is unknown. Typically, at the beginning of the growth period, parents notice findings such as shoulder asymmetry in the child, a bulge in part of the back, and hips that are not level.
Scoliosis is a sideways tilt of the spine of 10 degrees. In a normal, healthy spine, when viewed from behind, the vertebrae run straight from top to bottom in the neck, thoracic (back), and lumbar (waist) regions. In scoliosis, the vertebrae shift to the right or left and also rotate around their axis. For this reason, it is defined as a three-dimensional deformity.
Because of scoliosis, shifts occur in the hips, rib cage, and shoulder blades, in addition to posture and cosmetic disturbances. In adolescents, this abnormal loading on the developing spine leads to vertebral deformities.
The prevalence of scoliosis ranges from 0.2% to 6%. It is more frequent and more progressive in girls. It is observed in 1.5% of schoolchildren, and it is estimated that at least 150,000 children in Turkey have scoliosis.
This disorder, which is common in preschool boys, is 3–5 times more common in adolescent girls, depending on growth rate. Scoliosis, which usually does not cause prominent complaints early on, is often detected by school screenings or incidentally on X-rays taken for other reasons. Poor body appearance is one of the main reasons families consult a doctor. The first striking signs are asymmetry of the shoulders, shoulder blades, breast level, and waist folds. This may be accompanied by low back and back pain. With increasing curve magnitude, breathing difficulty may also occur.
What are the symptoms of scoliosis?
Scoliosis may show no symptoms in the early period. Even when symptoms appear, action is often not taken because complaints are minimal. For this reason, it is detected either in school screenings or incidentally on X-rays taken for any reason. The first finding that typically brings a family to the doctor is cosmetic asymmetry. The earliest observation in idiopathic scoliosis is that one shoulder is higher than the other. Asymmetry of the shoulders, breast level, waist or trunk folds are the first notable visual disturbances. Forty percent of cases have back and low-back pain. Curves over 50 degrees can cause breathing problems.
Scoliosis degrees
The natural course of scoliosis does not always remain the same. The spinal curve may progress, remain stable, or rarely improve. On two or more consecutive examinations, progression is defined as an increase of ≥5 degrees for curves over 20 degrees, and an increase of 10 degrees for curves under 20 degrees. Double curves, thoracic curves, female sex, larger curve magnitude at diagnosis, and curves diagnosed under age ten tend to progress. For curves under 30 degrees, the progression rate is very low. Scoliosis degrees are listed as follows:
Chronological classification
- Infancy: 0–2 years
- Juvenile: 3–9 years
- Adolescence: 10–17 years
- Adulthood: 18 years and older
By location
Anatomically, scoliosis can be classified as cervical, cervicothoracic, thoracic, thoracolumbar, and lumbar.
Angular classification
Imaging methods are used to quantify angular scoliosis. After imaging, spinal curvature is diagnosed by angle; this is especially useful in deciding on the need for surgery.
- Angles under 10°: termed “spinal asymmetry” and have no health impact. A curve must exceed 10° to be considered scoliosis requiring management. Low-grade curves do not pose a future scoliosis risk. The key is to determine whether the curve is progressing.
- Angles 20–40°: more common in adolescence. Considered moderate scoliosis; exercises, physiotherapy, and bracing are often very effective.
- Angles ≥40°: curves of 40° have largely completed growth and progression. Thoracic curves over 45–50° generally indicate surgery; for lumbar curves, 40° may be a threshold.
Causes of scoliosis
In 80% of patients, the cause of curvature cannot be identified. Structural causes include congenital vertebral anomalies; neuromuscular diseases (cerebral palsy, syringomyelia, poliomyelitis, myopathies); spinal tumors; trauma; spinal infections; and metabolic diseases. Postural disorders and leg length discrepancy are also causes. In brief:
- Congenital scoliosis due to vertebral malformations
- Infantile/juvenile scoliosis starting in early childhood
- Neuromuscular scoliosis from conditions like muscular dystrophy
- Connective tissue disorders (e.g., Marfan, Ehlers–Danlos)
- Scoliosis due to polio, inflammatory diseases, trauma
- Scoliosis from leg length inequality or hip/knee joint problems
How is scoliosis diagnosed?
Scoliosis can be diagnosed by examining the child. Asymmetry of the midline can be seen when viewing the bare back. When the child bends forward, lateral curvature and rib prominence on the opposite side become evident—this is called a rib hump. This may be harder to notice in some “balanced scoliosis” cases.
X-rays are obtained first to confirm spinal curvature, determine its magnitude and location, and see if there are associated bony anomalies. Scoliosis should be monitored with X-rays every six months. Other imaging (bone scan, CT, MRI) may be used for patients with neurologic findings or those planned for surgery.
Diagnosis is easily confirmed with plain radiography when scoliosis is suspected. MRI is rarely required. Because radiologic tests are used frequently in diagnosis and follow-up, the ovaries and breasts should be shielded with lead when imaging children.
Scoliosis curves are defined as primary and secondary. The apex (peak) is where the curve is most angled—i.e., the vertebra most rotated and farthest from the midline. Scoliosis is also named by the spinal level of the apex: cervical (neck), lumbar (low back), thoracic (mid-back). Sometimes multiple regions are involved; for example, when both thoracic and lumbar regions are affected, it is termed thoracolumbar scoliosis. It is most common in the thoracic region.
The shape and degree are determined on radiographs. The most commonly used measure is the Cobb angle. Treatment is guided by Cobb angle and growth stage. The Cobb angle is measured using lines along the upper endplate of the top vertebra of the curve and the lower endplate of the bottom vertebra; perpendiculars to these lines define the angle between the axes of those vertebrae.
Treatment of scoliosis
Scoliosis rarely regresses spontaneously. Early in growth, it is not possible to predict the course. Some recent studies show that children with certain genetic traits may progress. Important monitoring criteria guide treatment decisions. In some situations, progression is frequent and treatment success rates are lower, such as:
- High curve magnitude at first diagnosis
- Double curves (thoracic and lumbar)
- Neuromuscular scoliosis
- Severe muscle contracture and tightness
Treatment in Turkey is determined by the risk of curve progression. Accepted methods:
- Observation and regular follow-up
- Bracing (orthoses)
- Scoliosis-specific exercises and rehabilitation
- Surgery
If the Cobb angle is under 15° in children who have not yet started their growth spurt, specialized follow-up is usually recommended. For Cobb angles of 15–20°, scoliosis exercises and tailored rehabilitation should continue. Intensive rehabilitation programs are recommended for children with Cobb angles over 25°.
When early signs of puberty appear (hair growth, voice change, rapid height increase, breast development or onset of menstruation in girls), extra caution is needed and treatment is essential. Because curve velocity and risks are higher, progression risk—not just Cobb angle—should guide the plan. Children at high risk of progression should definitely use braces in addition to physiotherapy and rehabilitation. Bracing should continue 16–23 hours per day depending on growth status and curve magnitude until growth completion.
Surgical treatment may be applied if the Cobb angle exceeds 50° in individuals at high risk of progression where bracing fails. In scoliosis surgery, the spine is straightened centrally using rods and screws; these implants sometimes remain permanently. It should also be known that surgery can lead to late complications.
Role and effectiveness of bracing
Bracing is the most debated topic in scoliosis. Experts with different concepts hold varying opinions on its efficacy. A key reason is that properly designed, monitored, and curve-type-specific bracing is not uniformly known or applied in every country. Another reason is the resistance of growing children to wearing braces.
Technology has advanced greatly: braces can now be designed and fabricated with computer assistance, minimizing errors seen with classical techniques and achieving very successful results.
Braces used in scoliosis are called TLSO (Thoraco-Lumbo-Sacral Orthosis). They come in various types and models. Choosing and applying the correct brace model requires distinct expertise. The specialist must select the model, ensure timely additional corrections, and adjust pads during frequent follow-ups. Crucially, the team must also include experienced technicians who fabricate the brace correctly. In other words, scoliosis treatment requires teamwork: physician, technician, physiotherapist, family, and child must work together, monitoring every phase.
Scoliosis exercises
Scoliosis may be halted with exercise programs. These are highly effective especially for children ≥7 years with curves >15°. Good results are also seen in patients with curves >40°.
In addition to techniques like Bobath, Vojta, and Katharina Schroth, classic stretching and strengthening can be included. Considering the psychological factors in rehabilitation, intensive exercise programs have major benefits for adolescents. Group dynamics help teens connect with peers who share similar challenges.
Physiotherapy and rehabilitation applications
Rehabilitation programs with or without bracing are applied depending on timing in children with Cobb 20–30°. Those with 30–40° and adults with pain also benefit.
Several physiotherapy approaches are prominent: Vojta therapy, acupuncture, and the widely studied Schroth method. Details should be thoroughly explained to children and families, with clear guidance on required cooperation. Some programs are intensive; others run 3–4 sessions per week.
Intensive Rehabilitation for Spinal Deformity (SIR/YSR)
This customized, intensive program—arranged according to curve direction and individual factors—provides three-dimensional treatment based on proprioception and movement. The goal is to correct asymmetry and achieve appropriate posture in daily activities.
Patients referred from various locations join a 4–6 week program, 4 hours per day. For group sessions, patients with similar curve directions, magnitudes, and ages are grouped together; individual programs are used when needed. Core elements include breathing exercises; learning and maintaining correct posture via self-stimulating cues; curve correction with various balance and movement exercises; restoring normal balance and mobility; plus adjuncts such as orthotic concepts, stretching programs, massage, and swimming.
These programs are delivered by physiotherapists certified in the Katharina Schroth method. The aim is to educate patients about their condition, prevent curve progression, and maintain proper posture.
Scoliosis surgery in Turkey
Surgery is used for advanced cases or where the curve continues to increase despite exercises and bracing—or is expected to progress. In other words, if the Cobb angle increases despite conservative methods and exceeds 50°, surgery may be necessary. The decision should consider not only radiographic angle but also the patient’s psychological, social, and cultural context. Scoliosis during adolescence usually does not reach a level that damages the heart and lungs. Essentially, two surgical approaches are used: posterior and anterior. The posterior approach uses the back of the spine.
The goals of surgery are early monitoring of all patients, stopping progression, resolving cosmetic issues, and eliminating pain and neurological problems if present. When necessary, early interventions and simpler procedures may restore the spine. The most important point is performing the right surgery at the right time and protecting the spinal cord while correcting spinal and bony structure. With intraoperative imaging and neuro-monitoring tools that prevent injury to the cord and nerves, success rates are now very high. Treatment requires long-term follow-up and sustained communication between the care team and family.
Spinal mobility decreases after scoliosis surgery. In the anterior approach, the rib cage is accessed via the armpit area. Its drawback is that a postoperative brace is required; advantages include better preservation of spinal mobility and more aesthetic scarring (hidden under the arm).
Postoperative considerations and risks
As with any surgery, scoliosis operations carry certain risks—about 5% overall. If no complications occur, the patient can be discharged within 14 days. Undesirable outcomes may include:
- Infection, controllable with antibiotics
- Post-bleeding respiratory distress, relieved by draining accumulated blood
- Screw loosening or implant failure, requiring a second surgery
- Neurological deficit in <1% of cases (usually reversible)
Can scoliosis be treated without surgery?
الوقت المتطلب للقراءة 15 دقيقة
Yes, scoliosis (lateral curvature of the spine) can be treated without surgery in some cases, especially if the curve is mild or not causing significant health problems. Several non-surgical methods can help manage scoliosis:
-
Physical therapy: Can improve strength and flexibility in the spine and surrounding muscles. Specialized exercises may enhance posture and reduce pain.
-
Bracing (orthoses): In some cases—especially in children and adolescents who are still growing—braces can reduce the spinal curve and prevent it from worsening.
-
Medications: Pain relievers or anti-inflammatory drugs can be used to ease pain and inflammation that may accompany scoliosis.
-
Lifestyle changes: Such as regular exercise and avoiding activities that place additional stress on the spine.
If you have scoliosis or think you might, it’s best to consult a specialist for an accurate diagnosis and a treatment plan tailored to your condition.
إقرأ أيضاً
Addiction Treatment Center in Turkey
Steps of Liver Transplant Surgery and How Long a Patient Can Live After a Liver Transplant
Liver transplant in Turkey
Breast augmentation reduces neck and back pain.
Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS) Therapy in Turkey: A Modern Technique for Treati...
Psychological rehabilitation after addiction treatment in Turkey
The cost of addiction treatment in Turkey 2025: programs, services, and what the price includes
Success rate of kidney transplantation … how long does a kidney transplant recipient live?
هل يمكن علاج الجنف نهائيا؟
الوقت المتطلب للقراءة 15 دقيقة
The definitive treatment of scoliosis depends on the severity of the condition.
In mild cases, symptoms can be managed, and progression can be prevented with non-surgical treatments such as physical therapy or bracing, though the curvature itself may not change significantly.
In severe cases, surgery may be the only option to achieve a noticeable correction of the curve.
It is important to consult a specialist to determine the best treatment plan based on the individual’s specific condition.
إقرأ أيضاً
Sleeve gastrectomy in Turkey
Kidney Transplant with Robots in Turkey
Kidney transplant in Turkey
Gastric Sleeve Surgery in Turkey
Liver and kidney transplantation in Turkey
Psychological rehabilitation after addiction treatment in Turkey
Addiction treatment in Turkey: safe places for recovery and a specialized hospital
Rhinoplasty in Turkey and the best doctors for the procedure
How long does scoliosis treatment take?
الوقت المتطلب للقراءة 15 دقيقة
The duration of scoliosis treatment depends greatly on the severity of the condition and the type of treatment used. It can generally be summarized as follows:
- Physical therapy: May last for several months to years, depending on the patient’s response and progress. It involves regular sessions and home exercises.
- Bracing (orthoses): Typically used in children and adolescents with scoliosis, lasting for several years until bone growth is complete. Patients may need to wear the brace for several hours daily.
- Medications: Used to relieve pain and inflammation; duration may be short or long depending on the patient’s needs and response.
- Surgery: If surgical treatment is necessary, recovery may take several weeks to months, depending on the complexity of the procedure and the patient’s healing. After surgery, a long-term rehabilitation program is usually required to restore strength, flexibility, and normal movement.
In all cases, continuous follow-up with a specialist is essential to ensure that treatment aligns with the patient’s progress and needs.
إقرأ أيضاً
Psychotherapy for addiction in Turkey
Spinal surgery in Turkey | And the best spinal surgeons in Turkey
Breast Augmentation in Turkey: Available Options and Costs
Rhinoplasty and Dermal Fillers: A Comparison Between Cosmetic Options
Rhinoplasty in turkey - Some Important Tips After the Operation
Opium addiction and treatment
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) – Brain Battery
Strox Addiction Treatment
How do scoliosis patients sleep?
الوقت المتطلب للقراءة 15 دقيقة
Scoliosis can affect sleeping posture and make it difficult to find a comfortable position. Here are some tips that may help scoliosis patients sleep better:
- Choose the right pillow: Preferably one that supports the neck properly, keeping it in a neutral position with the spine. Memory foam pillows or specially designed cervical pillows may be helpful.
- Sleep on your back: This position can be comfortable for some patients. Placing an extra pillow under the knees can reduce pressure on the lower back.
- Sleep on your side: If side-sleeping feels better, place a pillow between the knees to support the spine and keep it aligned.
- Avoid sleeping on your stomach: This position can put extra pressure on the spine and worsen pain or discomfort.
- Use a proper mattress: A medium-firm mattress usually provides good spinal support. Avoid overly soft or overly hard mattresses.
- Consult a doctor: If scoliosis makes sleeping very difficult, it’s best to consult a specialist who can provide personalized recommendations.
You may need to try different positions and sleep aids to find what works best for you, as preferences vary depending on the severity and type of scoliosis.
إقرأ أيضاً
Crystal meth addiction treatment in Turkey
How Addiction Treatment in Turkey Can Restore Your Life — Under the Supervision of Dr. Alakkad
Kidney Disease Treatment in Turkey: Dialysis and Kidney Transplant
Spinal surgery in Turkey | And the best spinal surgeons in Turkey
Life after liver transplantation: what is it like? And tips for a better life
IVF and ICSI in Turkey
Prominent Ear Surgery Price in Istanbul: Information and Costs
Why Do Patients Choose Turkey for Addiction Treatment? Advantages, Services, and Modern Treatment Te...
Is walking beneficial for scoliosis?
الوقت المتطلب للقراءة 15 دقيقة
Yes, walking can be beneficial for scoliosis patients in several ways, but it should be done appropriately for each individual’s condition. Here are some potential benefits:
- Improves strength and flexibility: Walking helps strengthen back and core muscles, providing extra support for the spine. It also enhances overall body flexibility.
- Reduces pain: Light activity such as walking can help relieve some types of scoliosis-related pain by improving circulation and reducing muscle tension.
- Enhances balance: Walking boosts coordination and balance, which is helpful for scoliosis patients in maintaining proper body control.
- Supports general health: Walking promotes overall health and helps maintain a healthy weight, reducing pressure on the spine.
- Improves posture: Walking mindfully with proper body alignment can contribute to better posture, which is especially beneficial for those with scoliosis.
However, walking should be moderate and tailored to the patient’s needs. If you experience severe pain or limitations, it’s best to consult a doctor or physical therapist before starting a regular walking routine. They can guide you on the correct walking techniques and how to integrate walking with other treatments in your care plan.
إقرأ أيضاً
Success rate of kidney transplantation … how long does a kidney transplant recipient live?
Robotic Surgery Center in Turkey
Treatment of Eye Diseases in Turkey: Modern Techniques and Dr. Al-Akkad’s Role in Providing the Best...
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Injections – DPG PRP
Inverted nipple and treatment
Cocaine Addiction Treatment in Turkey
Eyelid Surgery (Blepharoplasty): Restoring Youthful Eyes at Turkish Aesthetic Centers
Cost of Kidney Transplant in Turkey | How Much Does a Kidney Transplant
Why does scoliosis pain get worse at night?
الوقت المتطلب للقراءة 15 دقيقة
The increase in scoliosis-related pain at night can occur for several reasons, including:
Spinal pressure: During sleep, the spine may be subjected to pressure or tension due to improper sleeping positions. This can worsen the pain if the posture does not provide proper support for the spine.
Muscle relaxation: At night, the muscles relax, which may reduce the support they provide to the spine. If the muscles surrounding the spine are weak or imbalanced, the pain may become more noticeable.
Lack of movement: Sleeping for long periods without changing position can cause stiffness in the muscles and joints. This stiffness may make the pain more noticeable upon waking.
Static position: Sitting or sleeping in one position for too long can cause strain on the muscles and ligaments, contributing to increased pain.
Temperature changes: Sometimes, changes in temperature or exposure to cold at night can worsen the pain, especially if the affected area is exposed to cold.
Sleep-related problems: Sleep issues such as insomnia or not getting enough rest can make the pain feel worse. Fatigue and lack of sleep can increase sensitivity to pain.
To relieve nighttime pain, try improving your sleeping position and using supportive pillows, such as those that support the back or neck. You may also want to try a comfortable, medium-firm mattress. Light exercises during the day can help relieve muscle tension and increase flexibility.
If the pain is severe or significantly affects sleep quality, it’s best to consult a specialist for an accurate evaluation and guidance on the best ways to manage the pain and improve sleep.
إقرأ أيضاً
Cost of Psychological Treatment in Istanbul: Programs, Services, and What the Price Includes
Breast Augmentation in Turkey: Available Options and Costs
Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) with Water Vapor Therapy
Crystal meth addiction treatment in Turkey
Infertility Treatment in Turkey: Advanced Techniques and Success Rates
Is addiction treatment in Turkey confidential and safe? Everything you need to know
Physiotherapy and Rehabilitation in Turkey: Specialized Centers and Services Provided
Kidney Disease Treatment in Turkey: Dialysis and Kidney Transplant
What causes scoliosis?
الوقت المتطلب للقراءة 15 دقيقة
Scoliosis is a lateral curvature of the spine and can be caused by a variety of factors. The causes of scoliosis are usually classified into two main types: primary (idiopathic) scoliosis and secondary scoliosis. Here are the causes of each type:
1. Primary (Idiopathic) Scoliosis
- Unknown cause: In most cases, the cause of idiopathic scoliosis is not known. It is believed that a combination of genetic and environmental factors contribute to its development.
- Genetic factors: There is evidence that scoliosis may have a hereditary link, as it can be more common in families with similar cases.
2. Secondary Scoliosis
- Congenital causes: Some cases of scoliosis occur due to problems in spinal development during pregnancy, such as incomplete growth of vertebrae.
- Neuromuscular causes: Scoliosis may result from neurological or muscular conditions that affect muscle control supporting the spine. Examples include cerebral palsy and muscular dystrophy.
- Injury- or disease-related causes: Scoliosis can result from spinal injuries or inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis.
- Degenerative causes: Scoliosis may develop in adults due to age-related spinal degeneration, such as degenerative disc disease or spondylolisthesis.
3. Unclassified Scoliosis
- Unconventional causes: In some cases, there may be less common or unclear reasons, such as scoliosis developing after injuries or surgery.
In all cases, if you suspect that you or someone you know may have scoliosis, it is important to consult a specialist doctor for an accurate diagnosis and to understand the causes and proper management of the condition.
إقرأ أيضاً
Is addiction treatment in Turkey confidential and safe? Everything you need to know
VASER Liposuction: Precise and Safe Body Contouring in Turkey
"Heart valve replacement in Turkey"
Cost of Psychological Treatment in Istanbul: Programs, Services, and What the Price Includes
Why Do Patients Choose Turkey for Addiction Treatment? Advantages, Services, and Modern Treatment Te...
Addiction treatment at home
Eyelid Surgery (Blepharoplasty): Restoring Youthful Eyes at Turkish Aesthetic Centers
العلاج الطبيعي وإعادة التأهيل في تركيا: المراكز المتخصصة والخدمات المقدمة
How do I know the degree of scoliosis?
الوقت المتطلب للقراءة 15 دقيقة
Determining the degree of scoliosis requires a thorough evaluation by an orthopedic specialist or a spine specialist. To assess the degree of scoliosis, doctors usually follow these steps:
1. Medical history and physical examination
- Medical history: The doctor begins by collecting information about the patient’s health history, symptoms, and any other medical conditions.
- Physical examination: This includes checking for spinal deformities, assessing the curvature, and evaluating the level of pain or discomfort.
2. X-rays
- X-rays: X-rays are considered one of the most important tools for assessing scoliosis. The patient is usually asked to stand in different positions (commonly standing while bending forward) to capture images showing the spinal curve.
- Cobb angle measurement: X-rays are used to determine the Cobb angle, which is the main method for measuring scoliosis severity. The Cobb angle is measured by identifying the most tilted vertebrae. The larger the angle, the more severe the curvature.
3. MRI or CT scan
- MRI: In some cases, an MRI may be requested to get additional details about soft tissues, such as the spinal cord and nerves.
- CT scan: This may also be used to obtain detailed information about the spine’s structure.
4. Functional evaluation
- Functional tests: In some cases, tests are performed to measure how scoliosis affects mobility and the ability to perform daily activities.
Scoliosis degree classification
- Mild: Cobb angle less than 20 degrees.
- Moderate: Cobb angle between 20 and 40 degrees.
- Severe: Cobb angle greater than 40 degrees.
If there are any signs or symptoms suggesting scoliosis, it is recommended to consult a specialist for an accurate diagnosis and a proper treatment plan.
إقرأ أيضاً
Butt Reduction and Fat Liposuction in Turkey: Information and Prices
Strox Addiction Treatment
Eyelid Surgery (Blepharoplasty): Restoring Youthful Eyes at Turkish Aesthetic Centers
Kidney Transplant in Turkey by robot
Treatment of Drug Addiction and Steps in an Addiction Treatment Center
Knee replacement in turkey
Bone Marrow Transplantation in Turkey
Cocaine Addiction Treatment in Turkey
هل الجنف يزداد مع تقدم العمر؟
الوقت المتطلب للقراءة 15 دقيقة
Scoliosis can worsen with age in some cases, especially if a person has degenerative scoliosis, which develops due to spinal wear and tear over time. Here are the main points about how aging affects scoliosis:
- Degenerative scoliosis
- Age-related changes: This type occurs because of natural deterioration of bones, spinal discs, and surrounding tissues. Disc degeneration or spondylolisthesis can worsen spinal curvature over the years.
- Age-related symptoms
- Pain and stiffness: With aging, symptoms like back pain and stiffness may increase as the spine and nearby muscles lose flexibility.
- Impact on flexibility and movement
- Reduced flexibility: Aging reduces spinal and muscular flexibility, which can worsen curvature and limit mobility.
- Effect of other health conditions
- Chronic diseases: Conditions such as arthritis or osteoporosis can increase the risk of scoliosis worsening with age.
Care and monitoring
- Regular check-ups: Continuous follow-up with a specialist is essential to track scoliosis progression and choose the best treatment.
- Conservative treatments: Physical therapy and tailored exercises often help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
👉 If scoliosis symptoms worsen as you age, it’s best to consult a spine specialist for a thorough evaluation and personalized care plan.
إقرأ أيضاً
The Cost of Liver Transplant in Turkey
Laparoscopic Gastric Bypass (R-YGB)
Heart Surgery Center in Turkey
Knee replacement in turkey
Gamma Knife Radiotherapy for Tumor Treatment in Turkey
VASER Liposuction: Precise and Safe Body Contouring in Turkey
Open Heart Surgery in Turkey
Facelift and Cosmetic Surgery in Istanbul: Modern Techniques and Expected Results
Does swimming treat spinal curvature?
الوقت المتطلب للقراءة 15 دقيقة
Swimming can be beneficial as part of a treatment program to help people with scoliosis, but it should be noted that it usually does not completely cure scoliosis or eliminate the spinal curvature entirely. Here’s how swimming can be helpful and why it may be included in a treatment plan:
Benefits of swimming for scoliosis
- Muscle strengthening: Swimming strengthens the back, abdominal, and side muscles, which helps support the spine and improve stability. Strengthening the muscles around the spine can reduce pain and improve posture.
- Improved flexibility: Swimming enhances overall body flexibility, which may help improve range of motion and reduce stiffness associated with scoliosis.
- Reduced pressure on joints: Water provides natural support to the body, reducing stress on the joints and spine during exercise. This can be especially helpful for those experiencing pain or discomfort due to scoliosis.
- Improved coordination and balance: Swimming helps improve coordination and balance, which is beneficial for people with scoliosis in enhancing mobility and preventing falls.
- Pain relief: Moderate physical activity like swimming can help relieve pain by improving circulation and reducing muscle tension.
Important considerations
- Consulting a doctor: Before starting any swimming program, it’s important to consult a specialist or physical therapist to ensure swimming is appropriate for your specific condition and to determine any special considerations.
- Suitable exercises: It may be helpful to focus on swimming exercises that avoid straining the spine, such as backstroke or moderate freestyle.
- Balance with other treatments: Swimming can be part of a comprehensive treatment plan that includes physical therapy, muscle-strengthening exercises, and other procedures as recommended by the doctor.
Overall, while swimming does not cure scoliosis permanently, it offers many benefits that can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
إقرأ أيضاً
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) – Brain Battery
Kidney Transplant in Turkey by robot
"Heart valve replacement in Turkey"
CAR T-cell Therapy and Its Side Effects
Gastric Sleeve Surgery in Turkey
Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease in Turkey
Duration of kidney transplantation surgery, its complications, success rate, and whether it is dange...
Treatment of cannabis addiction in Turkey
تكلفة جراحة الجنف في تركيا
أفضل جراحيين
The cost of scoliosis treatment in Turkey varies depending on several factors, such as the type of treatment, the severity of the condition, and the medical facilities used. In general, the cost of scoliosis treatment in Turkey is lower compared to many other countries, making it a preferred destination for many patients.
Dr. Al-Akkad, along with his distinguished medical team, is considered among the best in this field. Dr. Al-Akkad’s medical staff is well-known for their high competence and excellent medical services at the best prices. If you are looking for affordable scoliosis treatment with high quality, the cost of scoliosis treatment in Turkey, especially under the supervision of Dr. Al-Akkad’s medical team, offers you an outstanding option in the best hospitals.
